課程筆記
C5 數值方法-Bracketing Methods (界定法)
5.1 Graphical Methods
- 原理:用於求解方程式的根。(對於一連續可導方程式,當一區間的函數值為正負時,該區間內必至少有一個根(奇數個)。反之,若為同正貨同負,則無根或有偶數個根。)
- 然而,存在例外情況,如正好反曲點處為根。
- 優點:直觀、易於理解。
- 缺點:不精確、無法用於複雜方程式。
- 實施步驟:
- 畫出函數圖形。
- 確定根的大致位置。
- 進行縮小區間。
- 重複步驟 2 與 3,直到找到根。(記得有一位預估值)
5.2 Bisection Method (二分法)
- 原理:利用中值定理,將函數值為正負的區間進行二分,直到找到根。
連續可導函數,當 時, 於 之間必有根。
- 步驟:
- 確定
、 ,使得 。 - 計算
。 - 比較
: - 若
,則根位於 ,故 。 - 若
,則根位於 ,故 。 - 若
,則 即為根。
- 若
- 重複步驟 2 與 3,直至找到根或誤差可接受。
- 確定
- Approximate Percentage Relative Error (估計百分相對誤差,
): - 將算出的
與前一次的 進行比較。當 時(相對誤差小於停止誤差時),即可停止。 - 估計誤差必大於等於實際誤差。
- 將算出的
- 透過適當的選擇
與 ,可減少函數的計算次數。
5.3 False-Position Method (試位法/假位法)
- 原理:利用線性插值,將函數值為正負的區間進行插值,直至找到根。
- 步驟:
- 確定
、 ,使得 。 - 計算
: - 比較
: - 若
,則根位於 ,故 。 - 若
,則根位於 ,故 。 - 若
,則 即為根。
- 若
- 重複步驟 2 與 3,直至找到根或誤差可接受。
- 確定
Homework
題目
使用二分法與試位法求解此方程式的根。
解題流程
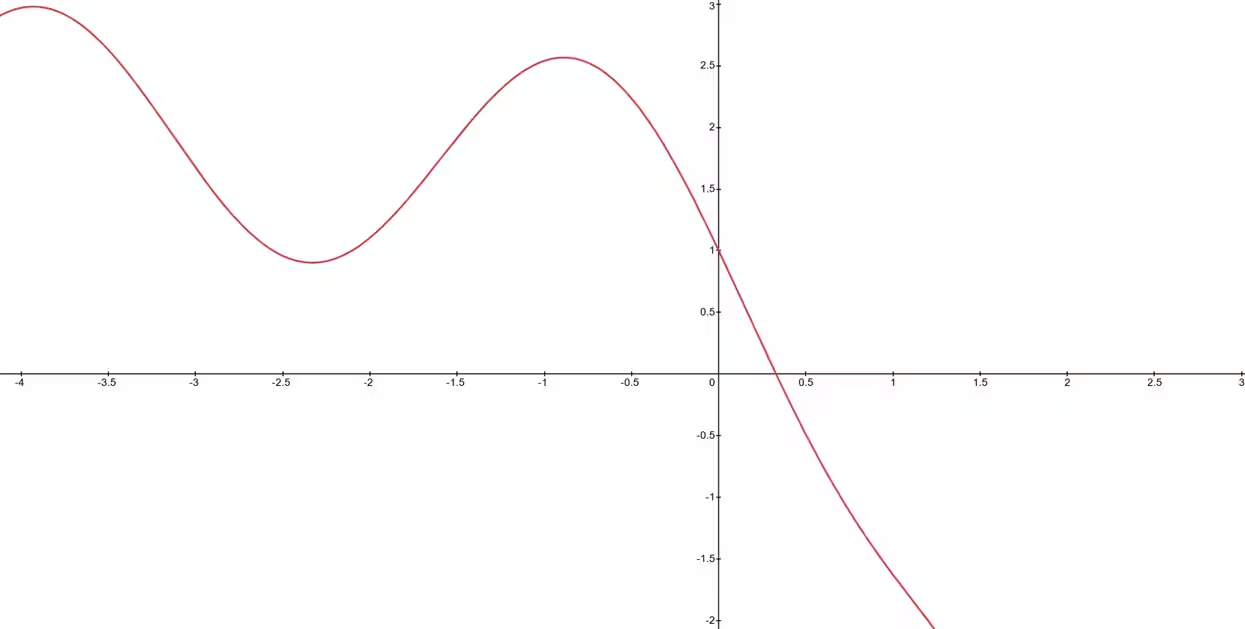
為求解方程式
先以繪圖法初步評估根的大致位置,如下圖。由圖可知,根約在 0.25 至 0.50 之間。故本次作業訂定 0.25、0.50 作為數值方法之上下界(
Code
並針對本作業撰寫 Golang 代碼如下所示。其中,定義 calcApproxError() 函數計算當前與前次疊代結果的相對誤差,用於判斷 calcBisectionMethod()、calcFalsePositionMethod() 分別使用 Bisection Method 與 False-Position Method 方法尋找根。輸入項包含欲求根之方程式 f、數值方法下界 x_l、數值方法上界 x_u、停止點誤差 epsilon_s,反覆疊代直至
而 Homework() 函數定義了於本作業中欲求得的方程式 calcBisectionMethod()、calcFalsePositionMethod() 於數值方法下界 x_l = 0.25、數值方法上界 x_u = 0.5、停止點誤差 epsilon_s = 0.005 之條件下求取方程式之根。最後,透過 main() 函數呼叫 Homework() 函數執行。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func calcApproxError(Current, Previous float64) float64 {
return math.Abs((Current - Previous) / Current)
}
func calcBisectionMethod(f func(float64) float64, x_l, x_u, epsilon_s float64) float64 {
// f is the function to find the root of
// x_l and x_u are the lower and upper bounds of the interval to search
times := 1
x_root_old := math.Inf(1)
x_root_new := (x_l + x_u) / 2
for calcApproxError(x_root_new, x_root_old) > epsilon_s {
fmt.Printf("Iteration %2d: x_l = %f, x_u = %f, x_root = %f, error_appr = %f\n", times, x_l, x_u, x_root_new, calcApproxError(x_root_new, x_root_old))
if f(x_l)*f(x_root_new) == 0 || calcApproxError(x_root_new, x_root_old) < epsilon_s {
break
} else if f(x_l)*f(x_root_new) < 0 {
x_u = x_root_new
} else {
x_l = x_root_new
}
x_root_old = x_root_new
x_root_new = (x_l + x_u) / 2
times++
}
fmt.Printf("Iteration %2d: x_l = %f, x_u = %f, x_root = %f, error_appr = %f\n", times, x_l, x_u, x_root_new, calcApproxError(x_root_new, x_root_old))
return x_root_new
}
func calcFalsePositionMethod(f func(float64) float64, x_l, x_u, epsilon_s float64) float64 {
// f is the function to find the root of
// x_l and x_u are the lower and upper bounds of the interval to search
times := 1
x_root_old := math.Inf(1)
x_root_new := x_u - (f(x_u)*(x_l-x_u))/(f(x_l)-f(x_u))
for calcApproxError(x_root_new, x_root_old) > epsilon_s {
fmt.Printf("Iteration %2d: x_l = %f, x_u = %f, x_root = %f, error_appr = %f\n", times, x_l, x_u, x_root_new, calcApproxError(x_root_new, x_root_old))
if f(x_l)*f(x_root_new) == 0 || calcApproxError(x_root_new, x_root_old) < epsilon_s {
break
} else if f(x_l)*f(x_root_new) < 0 {
x_u = x_root_new
} else {
x_l = x_root_new
}
x_root_old = x_root_new
x_root_new = x_u - (f(x_u)*(x_l-x_u))/(f(x_l)-f(x_u))
times++
}
fmt.Printf("Iteration %2d: x_l = %f, x_u = %f, x_root = %f, error_appr = %f\n", times, x_l, x_u, x_root_new, calcApproxError(x_root_new, x_root_old))
return x_root_new
}
func Homework() {
f := func(x float64) float64 {
// f(x) = 2 - sin(2x) - e^x
return 2 - math.Sin(2*x) - math.Exp(x)
}
fmt.Println("f(x) = 2 - sin(2x) - e^x")
fmt.Println("Bisection Method:")
fmt.Printf("Root is: %.10f\n", calcBisectionMethod(f, 0.25, 0.5, 0.005))
fmt.Println()
fmt.Println("False Position Method:")
fmt.Printf("Root is: %.10f\n", calcFalsePositionMethod(f, 0.25, 0.5, 0.005))
}
func main() {
Homework()
fmt.Scanln()// Wait for the user
}