Introduction
「人工智慧」一詞儘管現今常被使用,旨在模擬人類透過學習產生行為與決策的過程。人工智慧領域自二十世紀五零年代即開始發展,受益於演算法的突破以及數據蒐集與處理能力的提升,人工智慧技術於 2000 年迄今迅速發展。其中,人工智慧技術中普遍的關鍵技術包含機器學習、深度學習、強化學習、電腦視覺、自然語言處理、腦機介面等 (Zhang et al., 2021; Radanliev & Roure, 2021)。然而,多數民眾對這些技術理解有限,導致開發研究角色以及實際使用角色上的認知落差,甚至導致提升人工智慧領域勞動力提升的門檻。許多產學研界進一步投入提升沒有技術背景的潛在人才對於人工智慧的認知的工作 (Long & Magerko, 2020)。
人工智慧素養
人工智慧素養為一系列使人能夠批判性的評估人工智慧技術的能力。使個人能夠與人工智慧有效溝通以及協作。根據 Duri Long 與 Brian Magerko 歸納涵蓋以下五大主題以及十七項使用者技能 (Long & Magerko, 2020):
- 人工智慧是什麼?(What Is AI?)
- 認識人工智慧(Recognizing AI):理解人工智慧的各種型態,並能辨識其在日常生活中的應用。
- 理解智慧(Understanding Intelligence):理解智慧的本質,以及人工、人類智慧,甚至是動物智慧間的差異。
- 跨領域性(Interdisciplinarity):了解人工智慧如何結合不同學科的知識。
- 一般與專門人工智慧(General vs. Narrow):區分廣泛應用與專為特定任務設計的人工智慧。
- 人工智慧能做什麼?(What Can AI Do?)
- 人工智慧的優勢與弱點(AI’s Strengths & Weaknesses):辨識人工智慧在處理問題時的能力與限制。
- 想像未來的人工智慧(Imagine Future AI):推測人工智慧未來的發展與影響。
- 人工智慧如何運作?(How does AI work?)
- 知識表達(Representations):了解何謂「知識表達」,並能描述一些知識表達的例子。例如,一張圖片可以被表達為一矩陣,其中每個數值代表一個像素的顏色。(這種理解幫助我們知道,電腦如何將世界建模為它可以理解的形式,同時也認識到在這種表達中總會有一些知識的丟失。)
- 決策制定(Decision-Making):了解人工智慧如何做出決策,包括規劃、解決問題和學習。(可以幫助我們更好地理解和解釋算法。)
- 機器學習的步驟(Machine Learning Steps):理解機器學習涉及的步驟,以及每個步驟所帶來的實踐和挑戰。
- 人在人工智慧中的角色(Human Role in AI):認識到人類在編程、選擇模型、和微調人工智慧系統中扮演的關鍵角色。(學生常驚訝於機器學習需要人類決策,並非完全自動化。)
- 數據素養(Data Literacy):理解數據素養的基本概念,包括批判性的評估數據及其來源。(這對於理解機器學習至關重要,強調了基本數據科學概念作為人工智慧素養的一部分。)
- 從數據學習(Learning from Data):認識到電腦通常從數據(包括個人數據)中學習。
- 批判性地解讀數據(Critically Interpreting Data):了解數據不能僅憑表面數值接受,需要進行解讀。並理解初始數據集中的訓練範例如何影響算法的結果。
- 行動與反應(Action & Reaction):理解一些人工智慧系統具有物理作用於世界的能力。這種行動可以是高層次的推理(如按計劃路徑行走),也可以是反應性的(如感應到障礙後向後跳躍)。
- 感測器(Sensors):了解什麼是感測器,識別電腦如何使用感測器感知世界,並識別各種設備上的感測器。認識到不同的感測器支持對世界的不同類型的表達和推理。
- 應如何使用人工智慧?(How Should AI Be Used?)
- 倫理(Ethics):識別和描述人工智慧涉及的關鍵倫理問題,包括隱私、就業、錯誤信息、奇點(機器智慧超越人類智慧的假想時刻)、倫理決策、多樣性、偏見、透明度和責任等。這要求個體從不同角度考慮這些倫理問題,以及這些問題對社會的影響。
- 人們如何看待人工智慧?(How Do People Perceive AI?)
- 程式化(Programmability):理解人們可以通過編程來改變人工智慧的行為和功能的事實。
文獻計量檢視
22/02/2024 19:19 更新
於 2024 年 2 月 22 日,透過使用關鍵字「TS=(Artificial-Intelligen-Literacy OR AI-Literacy)」於 Web of Science Core Collection 資料庫進行檢索,得到 108 篇文章分布於 2019~2024 年間,如圖 1。
其中,108 篇文章來自於 74 個出版品,紀錄最多的出版品為 Education and Information Technologies 期刊,共包含 8 篇文章,詳如表 1。
| Sources | Articles Count |
|---|---|
| Education and Information Technologies | 8 |
| Education Sciences | 5 |
| Kunstliche Intelligenz | 4 |
| Sustainability | 4 |
| Educational Technology & Society | 3 |
| Information And Learning Sciences | 3 |
| International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education | 3 |
| British Journal of Educational Technology | 2 |
| Computers and Education Open | 2 |
| Computers in Human Behavior Reports | 2 |
根據 108 篇文章,可得知在全域引用(Global Cited)以及局部引用(Local Cited)最多的文章,如表 2 及表 3。
| Title | DOI | Total Citations |
|---|---|---|
| Trust, transparency, and openness: How inclusion of cultural values shapes Nordic national public policy strategies for artificial intelligence (AI) | 10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101421 | 60 |
| Developing an Artificial Intelligence–Enabled Health Care Practice: Rewiring Health Care Professions for Better Care | 10.1016/j.jmir.2019.09.010 | 44 |
| Perceptions of and Behavioral Intentions towards Learning Artificial Intelligence in Primary School Students | 找不到 | 38 |
| Are We Ready to Integrate Artificial Intelligence Literacy into Medical School Curriculum: Students and Faculty Survey | 10.1177/23821205211024078 | 34 |
| Promoting Students’ Well-Being by Developing Their Readiness for the Artificial Intelligence Age | 10.3390/su12166597 | 30 |
| Title | DOI | Local Citations | Global Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perceptions of and Behavioral Intentions towards Learning Artificial Intelligence in Primary School Students | 找不到 | 8 | 38 |
| Integrating Ethics and Career Futures with Technical Learning to Promote AI Literacy for Middle School Students: An Exploratory Study | 10.1007/s40593-022-00293-3 | 8 | 22 |
| Contextualizing AI Education for K-12 Students to Enhance Their Learning of AI Literacy Through Culturally Responsive Approaches | 10.1007/s13218-021-00737-3 | 7 | 18 |
| Measuring user competence in using artificial intelligence: validity and reliability of artificial intelligence literacy scale | 10.1080/0144929X.2022.2072768 | 7 | 16 |
| A review of AI teaching and learning from 2000 to 2020 | 10.1007/s10639-022-11491-w | 7 | 17 |
而由於以人工智慧素養為主題,文獻中出現詞頻最高的詞不僅在作者關鍵字或是摘要中,「人工智慧」以及「素養」皆能在前五名觀察到,如表 4。其中,作者關鍵字部分以生成式人工智慧佔據相對前端,除了前五個之後則以教育以及倫理為重。自摘要提取詞頻的結果則有所不同,單詞較為零散,僅提取一單詞時主要聚焦在人工智慧的教育以及技術運用。而提取二連續單詞時,則主要可觀察到包含人工智慧的教育面相以及生成式人工智慧。
| 作者關鍵字 | 詞頻 | 摘要(一詞) | 詞頻 | 摘要(二詞) | 詞頻 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ai literacy | 52 | ai | 729 | ai literacy | 201 |
| ai | 43 | literacy | 247 | ai | 96 |
| chatgpt | 14 | students | 243 | intelligence ai | 67 |
| generative ai | 11 | learning | 162 | ai technologies | 36 |
| literacy | 9 | education | 146 | ai education | 31 |
| ai education | 8 | study | 107 | generative ai | 18 |
| education | 7 | intelligence | 104 | machine learning | 18 |
| machine learning | 7 | artificial | 96 | health care | 17 |
| academic integrity | 4 | research | 85 | school students | 17 |
| artificial intelligence education | 4 | data | 78 | literacy education | 16 |
| early childhood education | 4 | teachers | 66 | students ai | 15 |
| ethics | 4 | understanding | 61 | computational thinking | 13 |
| computational thinking | 3 | teaching | 58 | ai tools | 12 |
| curriculum | 3 | technology | 55 | generative artificial | 12 |
| higher education | 3 | medical | 53 | students learning | 11 |
| information literacy | 3 | tools | 52 | ai knowledge | 10 |
| learning | 3 | development | 51 | digital literacy | 10 |
| pedagogy | 3 | technologies | 51 | factor analysis | 10 |
| perception | 3 | future | 47 | learning ai | 10 |
| university students | 3 | knowledge | 47 | students perceptions | 10 |
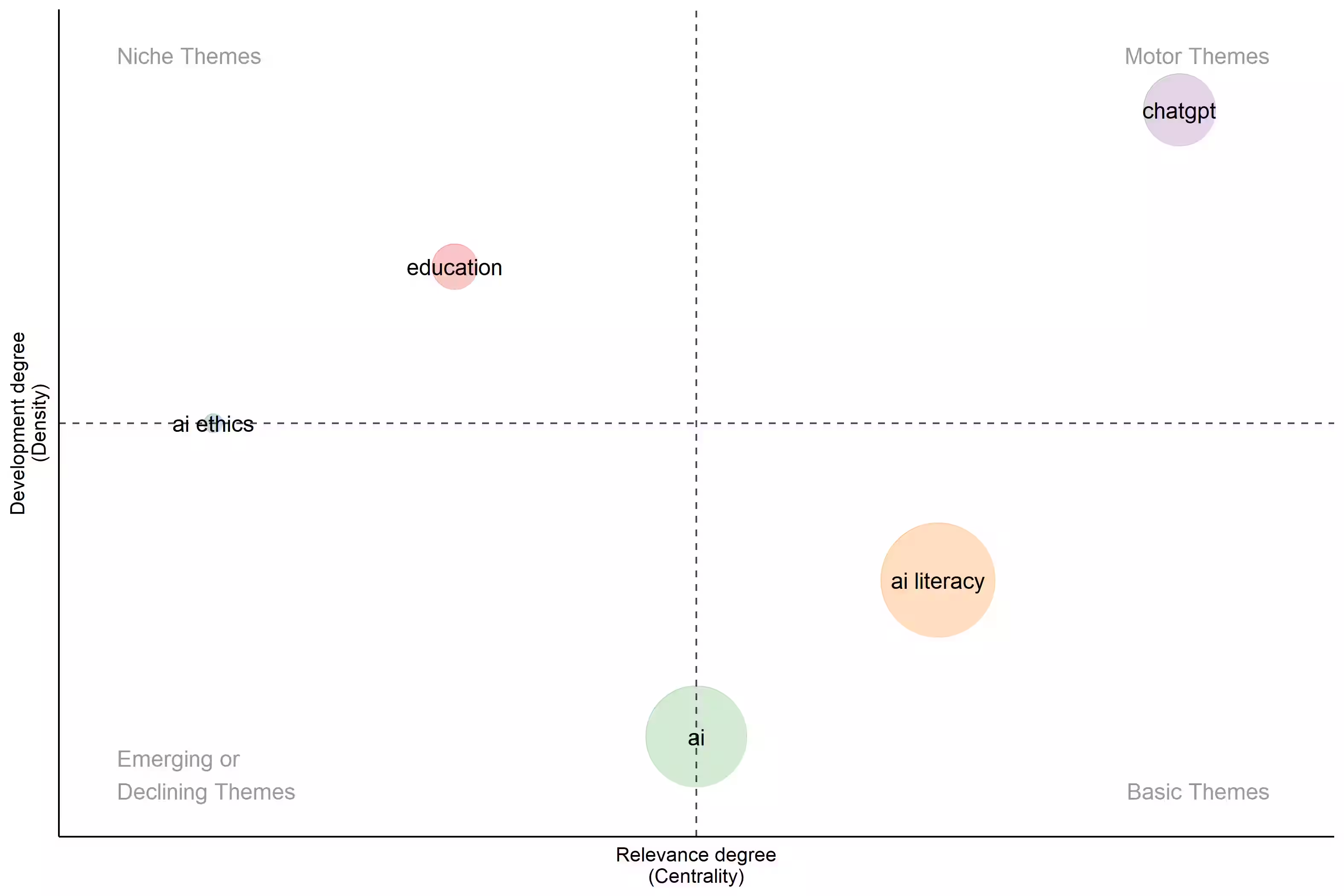
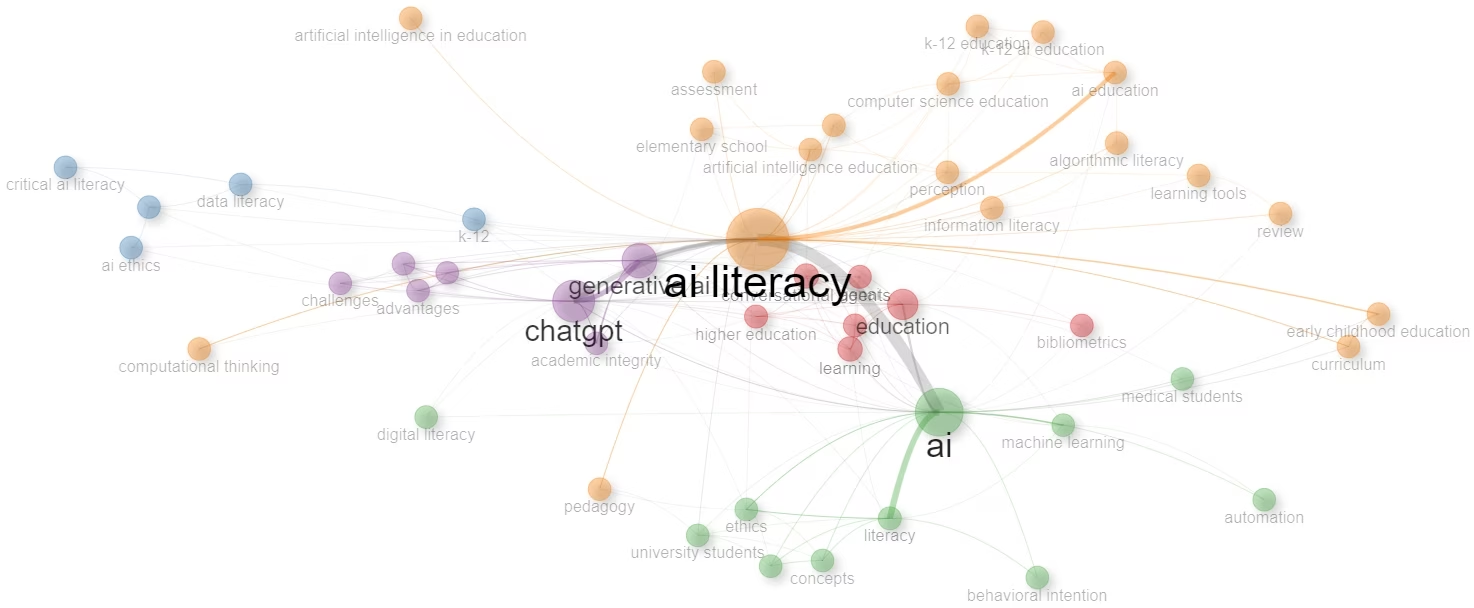
而將作者關鍵字透過密度及中心度劃分可得到專題地圖,詳如圖 2、圖 3(使用 Bibliometrix 套件繪製)。可以觀察到在人工智慧素養領域中最大者為人工智慧素養,人工智慧其次,接著為生成式人工智慧相關的 ChatGPT,以及教育與人工智慧倫理。
其中,人工智慧素養以及人工智慧的密度較低,為相對基礎的領域,而人工智慧領域中心性較低且密度更低,顯示在此領域人工智慧的技術在此領域以發展許多時間,深化應用並非目前發展重點。而生成式人工智慧的中心性及密度皆高,顯示為該領域目前的發展重點。而教育部分的發展密度高,顯示具有較高的發展程度。
References
- Long, D., & Magerko, B. (2020). What is AI Literacy? Competencies and Design Considerations. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. ACM.
- Radanliev, P., & de Roure, D. (2021). Review of Algorithms for Artificial Intelligence on Low Memory Devices. In IEEE Access (Vol. 9, pp. 109986–109993). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
- Zhang, Z., Song, X., Liu, L., Yin, J., Wang, Y., & Lan, D. (2021). Recent Advances in Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence Integration: Feasibility Analysis, Research Issues, Applications, Challenges, and Future Work. In N. Kumar (Ed.), Security and Communication Networks (Vol. 2021, pp. 1–15). Hindawi Limited.